In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a point object (an object so small that its mass can be assumed to exist at one point), or a non-rotating rigid body depends on themass of the body as well as its speed. The kinetic energy is equal to 1/2 the product of the mass and the square of the speed. In formula form:
where 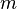 is the mass and
is the mass and  is the speed (or the velocity) of the body. In SI units (used for most modern scientific work), mass is measured in kilograms, speed in metres per second, and the resulting kinetic energy is in joules.
is the speed (or the velocity) of the body. In SI units (used for most modern scientific work), mass is measured in kilograms, speed in metres per second, and the resulting kinetic energy is in joules.
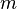 is the mass and
is the mass and  is the speed (or the velocity) of the body. In SI units (used for most modern scientific work), mass is measured in kilograms, speed in metres per second, and the resulting kinetic energy is in joules.
is the speed (or the velocity) of the body. In SI units (used for most modern scientific work), mass is measured in kilograms, speed in metres per second, and the resulting kinetic energy is in joules.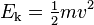
No comments:
Post a Comment